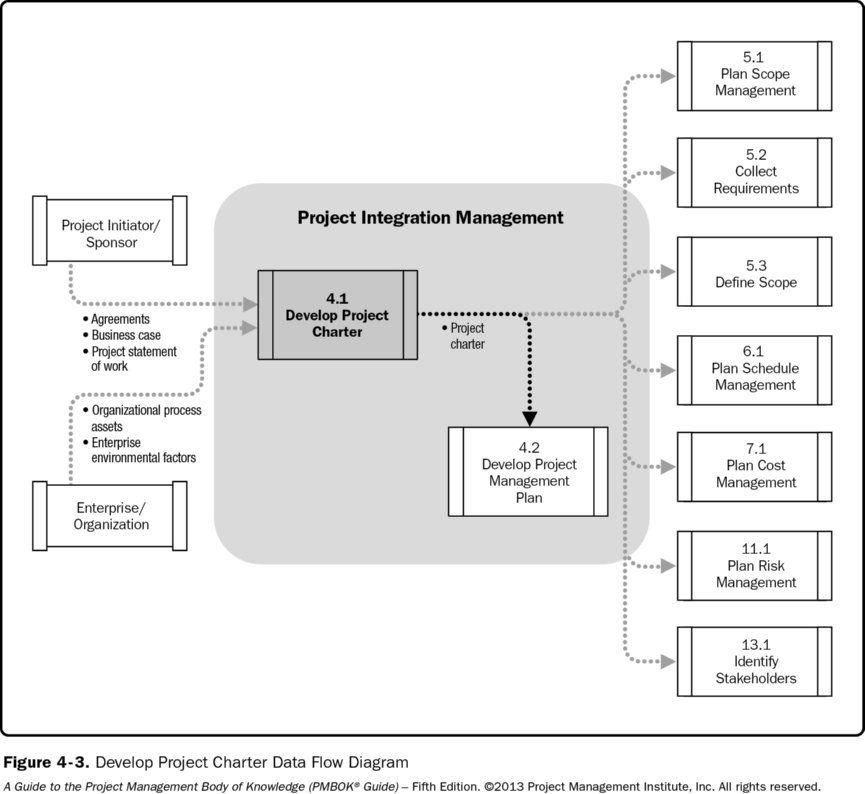
Value at Risk is a calculation that calculates the potential loss of investments. This calculates how much an investment will lose in a given day. It can also consider other factors like market volatility. This calculation is essential for all investors in stocks or bonds. This calculator can help you decide the best investments for your needs and risk tolerance. It is possible to use the value of risk calculation to plan for your retirement.
Probability of losing a certain amount by the amount of money being risked
When we invest, we use probabilities to determine the odds of success. There is a 12% chance we'll lose our $10,000 invested in stocks. Loss is the amount of money lost in case of failure. As an example, suppose we lose $5,000 on a investment. The damage would be $4000. It is important to understand that probability doesn't guarantee success.
Calculation VaR
When you invest, value at risk is an important tool that you should use to determine the amount of risk involved with a given investment. Based on past performance, the value at risk measure the likelihood of losing money. It also takes current market conditions into account. This can be used as a way to determine an average portfolio loss. The formula for calculating value at risc is very simple. The expected loss in 5% equals the portfolio's percentage value.
Monte Carlo method
The Monte Carlo method is a common tool in financial risk management. Because it allows for flexibility and a wide variety of scenarios, it is one of VAR's most powerful methods. Simulations can be used to account for complex pricing patterns as well as nonlinear exposures. This method also allows you to set longer time frames, which is necessary for risk measurement or model development. However, there are limitations to this approach.
Historical method
The Historical method of value at risk (VaR) is a popular approach in investing. It uses historical data as a basis for estimating risk factors. This data is then applied to current market values. It is an intuitive and simple way to calculate VaR. This corresponds to the maximum loss over a specific period. It is important to note that a VaR calculation is only as good as the number of correct data points it uses. To ensure accuracy, capture any changes in the market dynamics, such a major crisis.

Effects of VaR upon liquidity
Value at Risk, also known as VaR, measures an asset's riskiness. It is simply the ratio between the asset's current and expected future values. It is the most widely used measure of financial institution risk. It is based on a mathematical model that emphasizes rare events. The risk distribution can be parametric. This means that the mass of the distribution is at the mean and the tails are at a low point. For example, the FTSE Index has five such days over a 25-year span.
FAQ
What are some common mistakes managers make when managing people?
Sometimes, managers make their job more difficult than it is.
They may not delegate enough responsibilities to staff and fail to give them adequate support.
Additionally, many managers lack communication skills that are necessary to motivate and direct their teams.
Managers sometimes set unrealistic expectations of their teams.
Managers may attempt to solve all problems themselves, rather than delegating it to others.
What is the difference between management and leadership?
Leadership is about influencing others. Management is about controlling others.
A leader inspires his followers while a manager directs the workers.
Leaders motivate people to succeed; managers keep workers on track.
A leader develops people; a manager manages people.
Six Sigma is so beloved.
Six Sigma is easy and can deliver significant results. It provides a framework that allows for improvement and helps companies concentrate on what really matters.
What are management concepts, you ask?
Management concepts are the principles and practices used by managers to manage people, resources. They cover topics such as job descriptions and performance evaluations, human resource policies, training programs, employee motivation, compens systems, organizational structure, among others.
Statistics
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement a Quality Management Plan?
Quality Management Plan (QMP), which was introduced in ISO 9001:2008, provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products, and services through continual improvement. It is about how to continually measure, analyze, control, improve, and maintain customer satisfaction.
QMP is a common method to ensure business performance. QMP helps improve production, service delivery and customer relationships. QMPs should cover all three dimensions - Products, Processes, and Services. A "Process" QMP is one that only includes one aspect. QMP stands for Product/Service. If the QMP focuses on Customer Relationships, it's called a "Product" QMP.
Two main elements are required for the implementation of a QMP. They are Scope and Strategy. These elements can be defined as follows.
Scope: This is the scope of the QMP and its duration. For example, if you want to implement a QMP that lasts six months, then this scope will outline the activities done during the first six.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken towards achieving the goals set forth in the scope.
A typical QMP is composed of five phases: Planning Design, Development, Implementation and Maintenance. The following describes each phase.
Planning: In this stage, the objectives of the QMP are identified and prioritized. To get to know the expectations and requirements, all stakeholders are consulted. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: In this stage, the design team designs the vision and mission, strategies, as well as the tactics that will be required to successfully implement the QMP. These strategies are then put into practice by creating detailed plans.
Development: Here, the team develops the resources and capabilities that will support the successful implementation.
Implementation: This is the actual implementation and use of the QMP's planned strategies.
Maintenance: Maintaining the QMP over time is an ongoing effort.
In addition, several additional items must be included in the QMP:
Participation by Stakeholders is essential for the QMP's continued success. They need to be actively involved in the planning, design, development, implementation, and maintenance stages of the QMP.
Initiation of a Project: A clear understanding and application of the problem statement is crucial for initiating a project. This means that the initiator should know why they want something done and what they hope for from the end result.
Time frame: It is crucial to know the time frame for the QMP. For a short time, you can start with the simple version of the QMP. You may need to upgrade if you plan on implementing the QMP for a long time.
Cost Estimation: Cost estimation is another vital component of the QMP. You cannot plan without knowing how much money you will spend. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
QMPs should not be considered a static document. It changes with the company. It is important to review it periodically to ensure it meets all current requirements.